 FERMA-MOBILE
FERMA-MOBILE Microclimate controllers
Microclimate controllers Poultry weighing scales
Poultry weighing scales Silo scales
Silo scales Feed and water dispensing
Feed and water dispensing Lighting
Lighting Alarms
Alarms Extension modules
Extension modules Sensors
Sensors Accessories
Accessories Converters
Converters Separators
Separators Hermetic connectors
Hermetic connectors Installation boxes
Installation boxes Anti-disturbances filters
Anti-disturbances filters Servicing sets
Servicing sets The others
The others Software
Software Warranty terms
Warranty terms Download
DownloadGalvanic separators
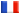
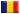
The RS232<=>RS232 galvanic separator is used to galvanic separation of TX, RX, RTS and CTS lines (for the RS-232<7>RS-232 separator also DSR, Carrier Detect) of the RS-232C interface and it ensures correct communication with speed of 116kbites/sec. The maximum level of separation voltage is 1000 V DC (700 V AC 50Hz). The signal lines are protected against over-voltage and the static charges by means of semiconductor protectors. The voltage levels are similar to the requirements of the RS232 standard (about 9V with supply voltage of 5V). Low power consumption enables a flexible choice of the source of supply (e.g. from the USB port of a PC computer).
Apart from standard usage, the separator can be used wherever there is need of separation of ‘ON/OFF’ type signals (including voltage levels on the separator’s lines). Then there can be used four one-way lines: two one-way (TX, RTS) and two the other way (RX, CTS) or seven one-way lines: three one-way (TX, RTS, DTR) and four the other way (RX, CTS DSR, Carrier Detect) in the RS-232<7>RS-232 separator.
Characteristics:
- transmission speed: 0 .. 116 kbites/s,
- separated lines: TX, RX, RTS, CTS,
- maximum level of galvanic separation: 1kVDC (700V, 50Hz),
- power supply:
- RS232<=>RS232: 5VDC±5%, stabilized (an external power supply unit is included in the set); RS-232<=>RS-233-DSUB9 12,5V unstabilized (DSUB9,PIN no 5: 0V, PIN no 9: +12,5V); RS-232<7>RS-232 5VDC±5%, stabilized (an external power supply unit is included in the set)
- power consumption: about 35 mA (on standby),
- a cable from the RS-232C side of about 1m length with a plug,
- D-SUB9 „female”, which enables direct connection of a converter to COM port of a PC computer,
- from the RS-232C side a socket D-SUB9 male,
- voltage levels similar to standard requirements: about- 9V as logical 1, about +9V as logical zero,
- power socket 5VDC round with a pin Φ 2,1 mm, plus at a pin,
- a housing made of plastic: 86 x 57 x 40 mm (dimensions are approximate, without sockets and a cable, length x width x height).






 Print
Print